Why glass panel use UV Resistant Ink
In industries ranging from consumer electronics to architectural design, Glass Panels serve as functional interfaces and aesthetic canvases. Yet, without UV-resistant ink, their longevity and visual integrity face critical threats. Here’s why specialized UV-blocking inks are non-negotiable:
- Preventing Color Degradation
Sunlight’s ultraviolet (UV) radiation breaks down organic pigments in standard inks, causing fading, yellowing, or color shifts within months. For example, a smartwatch dial printed with conventional ink may lose 40% color saturation after one year of daily UV exposure. UV-resistant inks integrate inorganic stabilizers (e.g., titanium dioxide) that absorb/reflect UV photons, preserving chromatic accuracy for 5+ years.
- Avoiding Adhesive Failure
UV rays weaken the polymer binders in screen-printed designs, leading to ink delamination. In automotive displays or outdoor Touch panels, temperature fluctuations exacerbate this issue, causing bubbles or peeling. UV-resistant formulations use cross-linked acrylic resins that maintain adhesion elasticity even at 80°C/176°F.
- ReducingSurface Embrittlement
When unprotected inks degrade, they create micro-cracks that compromise the structural cohesion of coated glass. UV-stable inks prevent this by incorporating nano-ceramic particles, which reinforce ink integrity against thermal stress and impact.
- Critical Applications Demanding UV Resistance
Consumer Electronics: Smartwatch bezels, smartphone logos, touch panel icons.
Automotive: Instrument cluster markings, heads-up display (HUD) layers.
Retail: Menu boards, shelf labels under LED/fluorescent lighting.
- Technical Composition & Testing Standards
High-performance UV-resistant inks blend:
① UV Absorbers: Benzotriazole compounds (e.g., Tinuvin®) absorbing 290–400 nm wavelengths.
② Hindered Amine Light Stabilizers (HALS): Neutralizing free radicals generated by UV exposure.
③ Inorganic Pigments: Cerium oxide for yellows, cobalt aluminate for blues.
Rigorous testing protocols include:
① QUV Accelerated Weathering: 800+ hours under UVB-313 lamps simulating 5 years of sunlight.
② ASTM D4587: Evaluating adhesion after UV/condensation cycles.
③ EN 12720: Chemical resistance against cleaners and solvents.
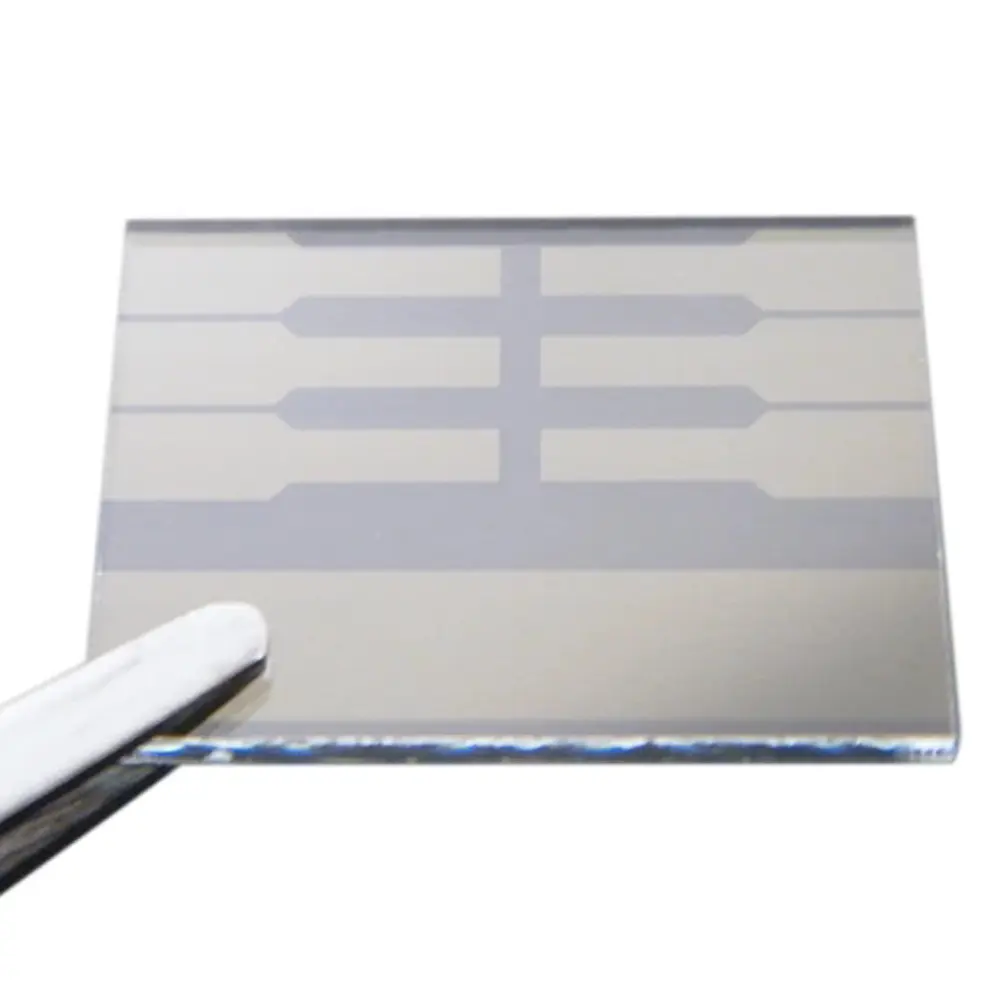
The Cost of Compromise
Using non-UV-stable inks risks:
- 30–60% faster product aesthetic failure.
- Increased warranty claims (e.g., faded brand logos on devices).
- Safety hazards in automotive/aviation where delaminated ink fragments may interfere with sensors.
For glass processors, UV-resistant inks are an investment in durability—transforming glass from a vulnerable substrate into a resilient, lasting interface. As UV exposure intensifies globally, this technology bridges aesthetics and endurance.
For further discussion, please feel free to contact us: sales@saidavn.com


 Phone
Phone Send Email
Send Email whatsapp
whatsapp Facebook
Facebook